There has been an ever-increasing focus on how buildings are built and renovated to maximize energy efficiency and waste with as few materials and resources as possible, while still maintaining, or even increasing overall function. The effort is commonly referred to as “green building” or “green design,” owing to the term “green,” which traditionally implies a cost and resource analysis that studies the entire lifecycle of the product/structure, with an emphasis on environmental responsibility. It’s also grossly misused for marketing purposes, but that’s besides the point.
The why question is obvious: we use vastly too many resources. The Global Footprint Network, a research organization, produces some interesting and shocking indexes for countries and regions of the world, called “Ecological Footprints,” that measure the use of resources against what the Earth regeneratively provides. The current World Footprint shows that humans use around 50% more per year than the Earth can regeneratively provide in the same period, a situation termed “overshoot”. Worse yet, our usage exacerbates the stability of the climate, so the regenerative capacity is also declining. The measure is quite clever, since it’s the same term we apply to budgeting, so a logical comparison is that the Earth provides us with a budget, and we overspend it worse than the US Congress.
Buildings and transportation account for over 75% of this spending in the United States. Transportations costs are closely tied to land use, which is another topic, but building energy consumption is largely a result of lighting, cooling, heating, electronics, ventilation, water heating, refrigeration, and various other activities. The intent of green design is to minimize a building’s demand for energy and resources in order to fulfill these various activities.
Perhaps the most widely-used system for measuring these design strategies is called LEED, which stands for Leadership in Energy & Environmental Design, created and administered by the US Green Building Council. The system awards points for various design features within a project, ranging from simple features like bike racks to more advanced systems like geothermal heating. The number of points determines the level at which a project (or existing building that has been commissioned) is rated: from certified to silver, gold, and platinum. LEED has several types of rating systems based on the type of project.
Just recently announced, the Tompkins County Legislature will be asking for public comment on a proposed law to grant partial property tax incentives to projects that qualify for LEED certification. The meeting is this Thursday, February 6th; below is the proposed resolution: My apologies, I was mistaken: public hearing is February 18th, 5:30pm, in the Tompkins Legislature Chambers The public hearing has been postponed since the resolution was sent back to committee level this past Thursday’s meeting, the 6th.

The legislation passed in the New York Legislature earlier this year to allow municipalities to enact- in New York State, property tax abatements can only be authorized through the State Legislature, and in this case, Tompkins County will be deciding whether or not to enact this section. The legislative intent is to help defray the cost of commissioning a LEED building (fees, design review, design premium, etc.), which can vary depending on the project’s cost and complexity. The 2003 cost study I am citing is by Greg Katz, of Capital E.
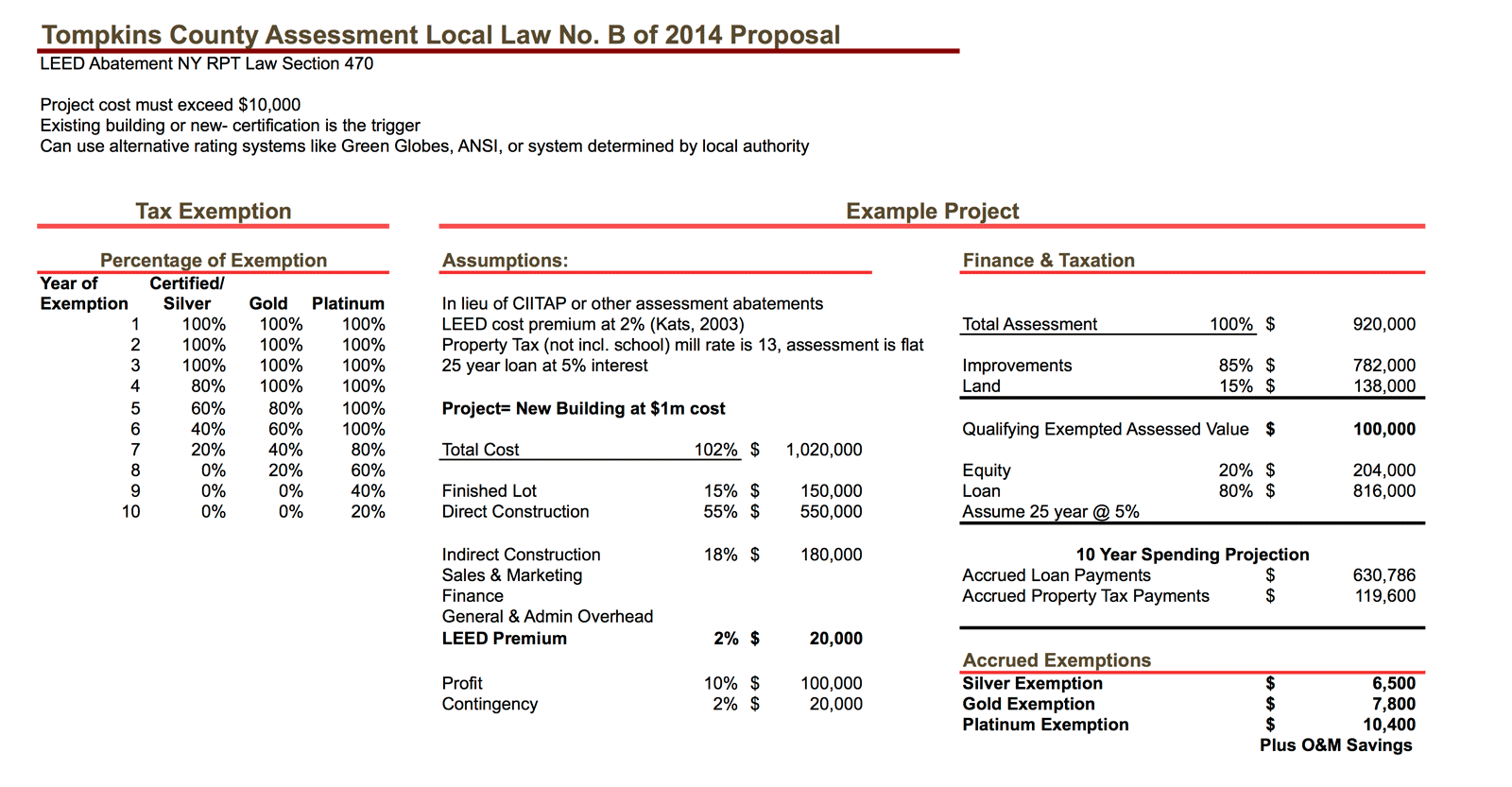
The proposed abatement would incentivize existing buildings to undergo renovations and commissioning through the LEED system to gain certification, and would also incentivize new projects to add green design to their plans. I put together a simplistic model below to show the impact on an example $1 million project, along with some of the requirements as pointed out in the law. The proposed legislation aims for a $100,000 cap in abated assessed improved value per the LEED project, applying only to Tompkins County property taxes.
The US Green Building Council is broken-up into chapters, and Upstate New York has its own chapter, which reviews projects, organizes events, educational materials, coordinates among design professionals, and perhaps most importantly- uses the practice and experience of LEED professionals within the chapter to issue guidance on the rating system and proposed improvements to the national organization. There are some great practical training opportunities for those interested through GPRO (Green Professionals), which also just received a grant from NYSERDA to provide further training sessions throughout New York State.
Many architects and design professionals already have experience with green design, and interestingly enough, an Ithaca-native will be releasing what may indeed become a standard reference in the field:

Green Building Illustrated is being released this month, authored by Francis D.K. Ching and Ian Shapiro, Chairman of Ithaca-based Taitem Engineering, PC. Taitem is an award-winning, and often published design and engineering firm, which recently became a fully-certified B Corporation back in May 2013.
I asked Ian about his history as a design and engineering professional, and how the book came about in order to share it here:
Ian Shapiro: I am not an architect, but I have always loved technical drawing. In high school, I took drawing classes from a wonderful old Scandinavian immigrant, and I still have those pencil drawings. In college, I took drafting classes from a Professor Zsombor-Murray at McGill, a real character, with a big beard, a difficult professor, and a stickler for detail.
I always found that drawing brought me great calm. I would come out of drawing classes with a wonderful, peaceful feeling.
After college, I moved home to the New York City area from Montreal, and started grad school at Columbia. Around this time, I believe in a used bookstore, I happened on an early copy of Architectural Graphics, by Francis D.K. Ching. I’m almost certain it was the first edition, smaller than it is now, published at that time by Van Nostrand Reinhold, which was subsequently bought by John Wiley and Sons. I was taken by the straightforward instructions and by the clarity: Make sure two lines meet; show people in a relaxed poses; so much more. I took the book and practiced drawing from it – shading, lettering, and more. I still have my notebook from those exercises. I started sketching buildings just for fun – cabins I stayed in on vacation, homes I lived in, and more. I used these sketching techniques when designing prototype heat pumps while working at Carrier Corporation.
After a few years working for Carrier, I started Taitem Engineering. Taitem stands for “Technology As If the Earth Mattered”. The name derives from the subtitle to the book Small is Beautiful: Economics As If People Mattered, by E.F. Schumacher, which I read when I was at McGill. Today, Taitem is a 40-person consulting company, recognized for its work in energy conservation, engineering design for buildings, and renewable energy.
When I started Taitem, I illustrated my own reports, at that time I was using an early CAD program. I don’t regard my drawing capabilities as anything but simple, but I have a deep love for line drawings, that goes way back over four decades. I treasured Architectural Graphics, and still do. Over the years, I picked up other books by Frank Ching, and am simply in awe of the breadth of the work. I have my favorites, I’m thinking of Architecture: Form, Space and Order for example, but I love them all. It’s not only the drawings, the crispness and clarity of the text is just something else.
So this is how I came to think of Frank when someone suggested that a book on green building design needed to have illustrations.
About 30 years after reading Architectural Graphics, I reached out to Frank Ching and asked him if he would co-author a book on green buildings. He had recently retired from teaching at the University of Washington. He graciously agreed. Frank’s body of published work in architecture is unrivaled. His books are translated into over 15 languages around the world. It was a great honor and pleasure to work with him.
If you’re interested in the book, it can still be pre-ordered through Amazon until February 24th when it’s released for general sale, and also ordered through the publisher, John Wiley & Sons. As a personal endorsement, I own three Frank Ching books, and they’re a tremendously helpful professional resource- this book should be no different.
Part Two of this post shall feature information on a few local efforts, as well as a section on the System Benefit Charge, a funding mechanism in New York State that charges energy consumers a fee on their usage in order to fund energy-efficiency incentive programs through NYSERDA as part of New York State’s Renewable Portfolio Standard.
































